【睡眠檢測】要怎麼做呢?有哪些要注意?檢測的5個步驟
15.05.2021
【向睡眠中心預約】
睡眠檢測需事先向醫院的睡眠中心預約,通常約需等待3~4週時間(可見越來越多人有睡眠問題!)
【報到、填寫問卷】
檢查當天都是晚上10:00~11:00 報到,檢測前填寫一份睡眠狀況問卷。
【睡眠檢測室環境】
檢測室都是一人一間,有對講機、監視器及小夜燈。
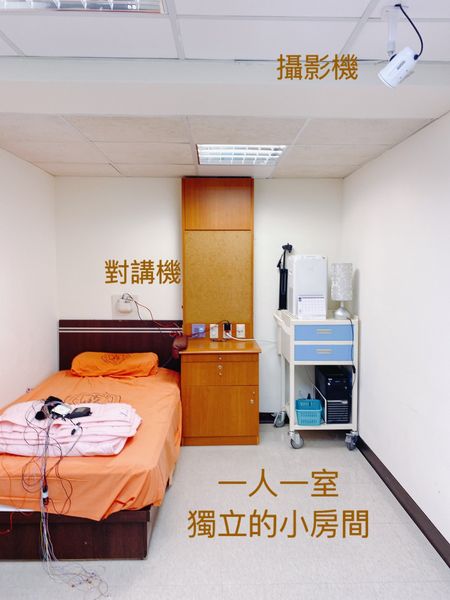
▲睡眠檢測室環境
【睡眠檢測的5步驟】
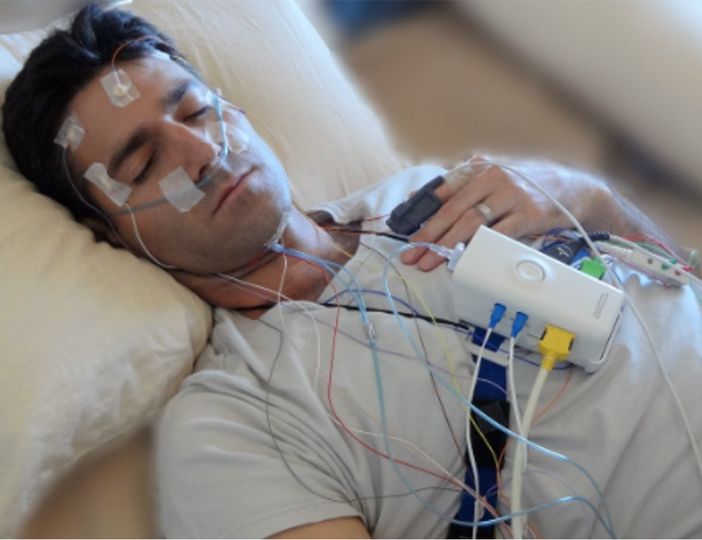
上完洗手間準備就緒,醫護人員就會進入房間內開始裝上檢測裝置:- 檢測人員會先幫你量測腰圍及頭圍,接著在頭部(請事先將頭皮乾淨才不會抗阻喔!)、臉部、身上及小腿貼上檢測感應線,然後在胸部及腹部分別繫上束帶,這時可以起身走動看看是否有任何不適。
- 接著躺下來,工作人員會在你的鼻孔安裝兩條氣流強度偵測管(採拋棄式),最後夾中指量測血氧飽和濃度。
- 安裝完畢後,醫檢人員離開房間,接下來用對講機請你配合指令做出動作。
- 關燈睡覺檢測開始,直到隔日清晨5~6點喚醒(如果半夜想上上廁所的話要按鈴告知工作人員先卸除檢測裝置)
- 檢測裝置卸除後,最後還需填寫測試後的問卷,才算完成睡眠檢測喔!大約等待一週的時間報告就會出來!

▲睡眠檢測裝備
【睡眠檢測結果的判讀】
我們常說的睡眠檢測就是:睡眠檢測到檢測內容的產生,過程其實就是一系列的睡眠多項生理檢查(Polysomnography),包含眼動圖、下顎肌電圖、鼾聲、心電圖、口鼻呼吸氣流、胸腹起伏狀態、睡眠狀態血中含氧濃度、睡覺的姿勢等監測。每30秒為一個單位,連續紀錄6個小時的睡眠數據,一個晚上下來就會有720份的記錄單位,可以客觀的知道夜晚熟睡期、淺眠期、快速動眼期所占的比例,以及了解是否有打鼾、睡眠呼吸中止或是有睡眠週期性肢體抖動症的問題存在!而檢測報告的判讀,是需要專業的醫師來進行判斷的,若大家對自己的睡眠狀況有任何的問題,也歡迎來找劉醫師諮詢唷!